What is Competency Modeling?
If you work in Human Resources or are a CEO who keeps up to date with learning and development program trends, you will know of competency models. A competency model, according to TrainingIndustry.com, is “a framework for defining the skill and knowledge requirements of a job. It is a collection of competencies that jointly define successful job performance.”
Competencies are more all-encompassing than job skills because the idea is they take into account soft skills such as knowledge, behaviors, and abilities in addition to technical or required skills of a role. And this collection of competencies makes up a competency model.
Whether your company needs to assess hard or soft skills for business goals or due to compliance with quality and safety regulations, implementing competency models within your organization will supercharge your learning and development program.
Elements of a Competency Model
Competency models can take a variety of forms, but as CareerOneStop.org points out in the excerpt below, they usually include the following elements:
- Competency names and detailed definitions
- Descriptions of activities or behavior
- A diagram of the model
For example, a competency model could include a competency called “Teamwork” defined as:
- establishing constructive and solid interpersonal relationships;
- treating others with courtesy, tact, and respect;
- working effectively with others, regardless of organizational level, background, gender, race, or ethnicity;
- working to resolve disagreements, attempting to persuade others and read agreements;
- abiding by and supporting group decisions; and
- facilitating team interaction and maintaining focus on group goals.
And this model of Teamwork could consist of behaviors such as:
- handling differences in work styles effectively when working with coworkers,
- capitalizing on the strengths of others on a team to get work done,
- anticipating potential conflicts and addressing them directly and effectively,
- motivating others to contribute opinions and suggestions, and
- demonstrating a personal commitment to group goals.
While these models can often be as simple as a bulleted list, a visual diagram can help leadership and direct reports get a better sense of how the competencies are interrelated and their key features. They can also include information on career pathways and how the requirements of the hard or soft skills are different at various levels of mastery and experience.
Look at this competency model from CareerOneStop.org as an example. It is the Waste and Wastewater model. And to learn more about manufacturing and competency management, read our article on the topic.
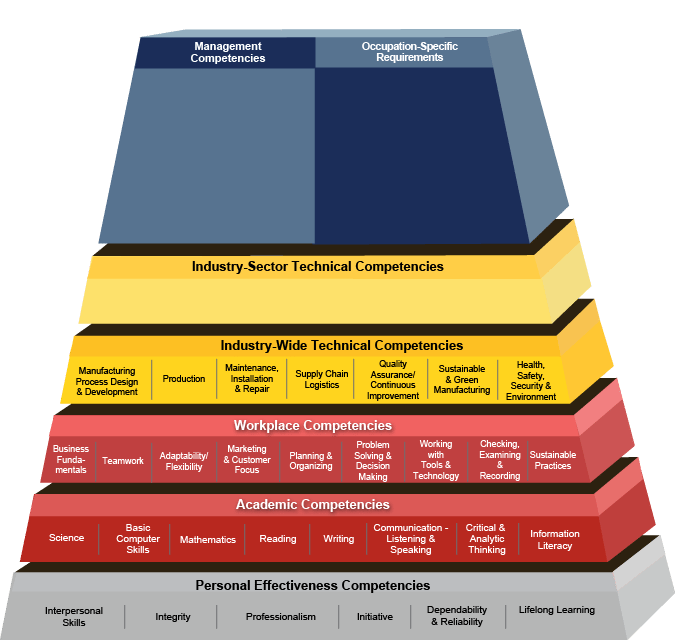
Once the model has been put in place, there are many different ways to implement it into an organization. Many companies use elearning and training software such as Learning Management Systems (LMS). More advanced companies use Competency Management Systems. See a few examples of this below.
Competency-based Training Example in Manufacturing
Human resources and training departments use competency models to define skill requirements for specific positions. These models are also used to assess performance and job progress, and in this way, help set business strategy throughout the company as a whole.
For example, The Manufacturing Institute has developed the Advanced Manufacturing Competency Model. In this model, some of the workplace competencies include:
- Understand how one’s performance can impact the success of the organization
- Demonstrate an understanding of market trends, the company’s position in the marketplace, and defined market segments
- Understand the position of the company’s products/services with regard to market demand.
Any worker possessing the above competencies will make them a more valuable employee. And as you can see, workplace competencies encompass much more than the technical skills required for job performance. In this Advanced Competency Model, we also include issues related to business ethics, legal/financial issues, environmental, health and safety, and social responsibility issues.
Competency Model Example in Human Resources
Not all competency models have to be industry-specific and can have broader use to Human Resources as well. Assessment Associates International, a recruiting firm, recently noted, “Organizations are fluid and dynamic. Technologies and processes change, and competitive pressures regularly alter how jobs are defined. Less supervision, increased technical skills, greater use of information technology, and the ever-changing nature of work itself all create a need for a different set of competencies.”
AAI also goes on to describe how competency models can not only help with the learning and development of current employees but can aid in the process of hiring to determine what to look for in a candidate and career pathways for each individual from day one. Look at their version of a competency model below, and notice the similarities and differences from the one that CareerOneStop put together.
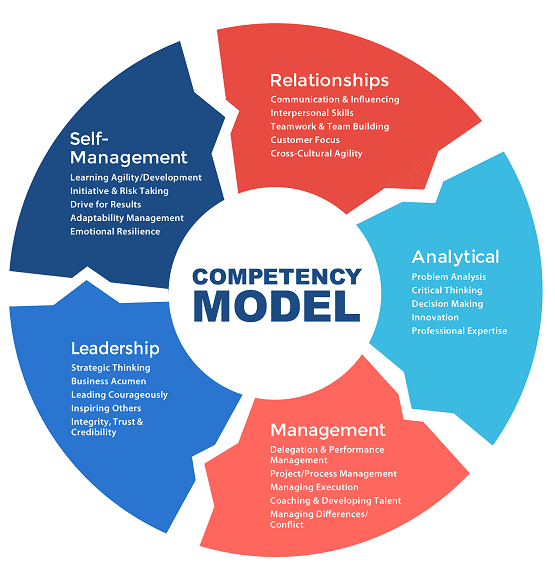
Value of a Competency Model
While it is true that all companies already have some sort of competency management program in place because if their employees weren’t competent they would be out of business! But the purpose of a competency management system and competency modeling is to identify what makes the best members of the organization special and translate that to the rest of the business. Cheryl Lasse for TD.org specifies that “In essence, the value of a competency model is that it identifies what skills each person in the company must be able to do to be “great.” If everyone performs at the “great” level, the company strategy is achieved, and a company is likely to have a competitive advantage. For example, an engineer must be able to perform engineering design functions, but a great engineer can work with other R&D engineers to troubleshoot design issues before they reach manufacturing.”
Bear in mind that in today’s competitive business environment, the need for competency models is more acute than ever. Lasse goes on to elaborate this point, saying:
- The pace of change has accelerated—and with it, the skills required to be successful continue to change.
- To survive today, companies must continuously innovate, which only increases the changing skills required.
- People stay in the same job for less time and, therefore, people need to be able to become “great” without as much experience as they had in the past.
- New workers entering the workforce want to be able to make an impact more quickly; they want to know how to be “great” right away and are motivated to get there.
Managers need to know what hard and soft skills are required for themselves and their direct reports to excel. They must also understand how to innovate and maximize their talent management potential. This leads to more motivated individuals and success for the organization.
How to Use Competency Models in Your Organization
Now that you understand what a competency model is, have seen examples, and how they are valuable to an organization, it is time to make them for yourself! To use competency models, it is important to identify who the key instructional designers and subject matter experts are in your organization. This personnel will be instrumental in not only creating the models but also distributing them to the organization and making sure they are implemented effectively. Depending on the type of organization, these individuals could all be in the HR department, but it is likely they are in the Learning and Development department, as well as some members in the Quality and Safety divisions.
Many organizations use a combination of spreadsheets and written documents to write down the competency models, and then put the onus on L+D leadership to carry them out to the rest of the organization using an LMS.
This can be effective, but as organizations grow and requirements change, can become problematic. To learn more about the importance of Competency Management in an organization, read our article.
Here at CABEM, we believe that the best way to positively impact your employees and learning and development programs is with a competency management software system. We designed our Competency Manager product for this exact reason. If you see value in this type of approach and want to learn more, we’d love to give you a demo.
Other articles that may interest you:

